
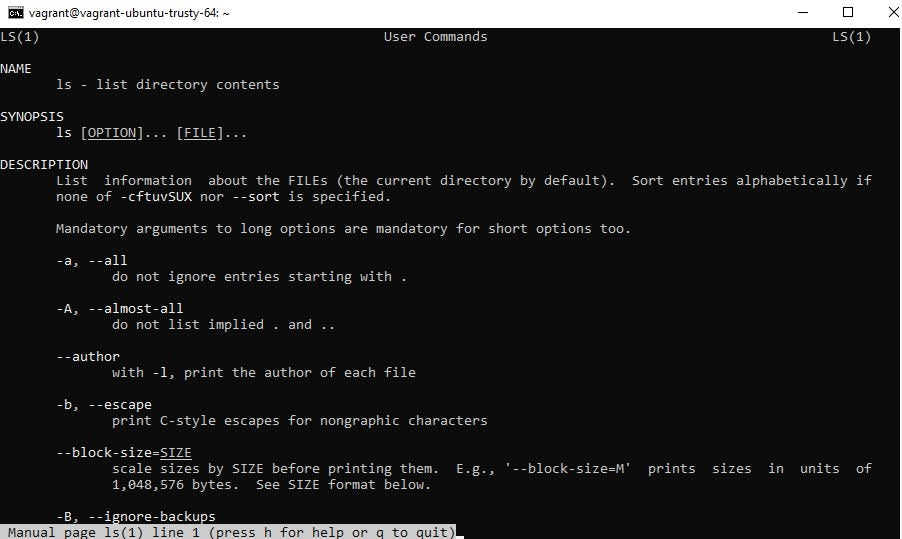
This command will display the current working directory. The name of the current logged on user will be displayed. This command is used to display who is the current logged on user. This command will list all the files which start with the word ‘Sample’. In this example, we will issue the following command. The files based on the file pattern will be displayed. Syntaxįilepattern − This is the pattern used to find for files. We can use the find command to find for files. The output will contain information on the ls command. If we issue the ‘ man ls’ command, we will get the following output. Exampleįollowing is an example of the ‘man’ command. The information on the command will be displayed. SyntaxĬommandname − This is the name of the command for which more information is required. To get more information on a command, we can use the ‘ man’ command. To clear the screen, we can use the clear command. This is shown in the following screenshot with the ls –l command. The directory listing of the current directory will be shown as the output.Īnother variant of the ls command is to list the directory, but with more details on each line item.
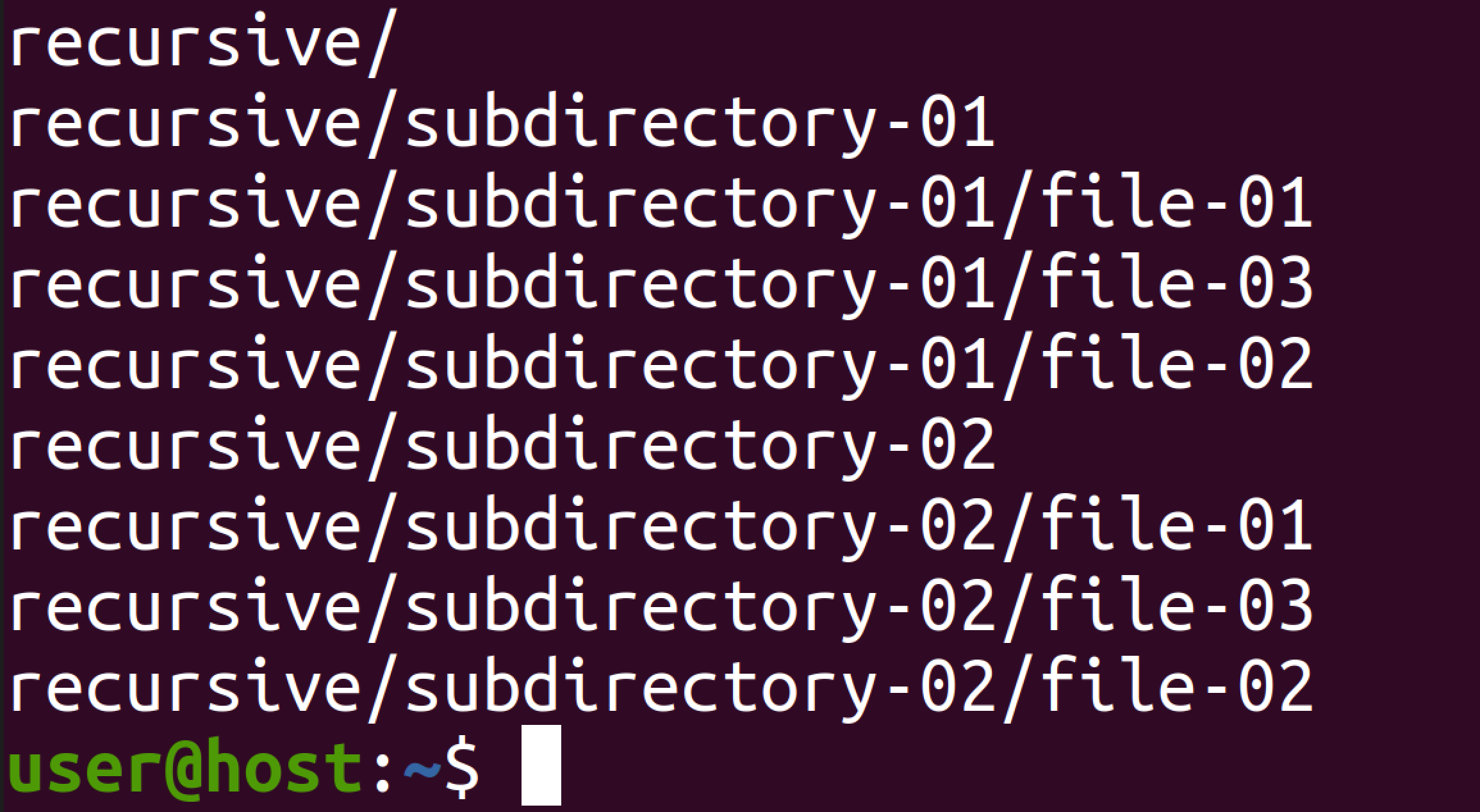
In the following example, we just issue the ls command to list the directory contents. The output will be the listing of the directory contents. Option − These are the options to be specified with the ls command.ĭirectoryname − This is the optional directory name that can be specified along with the ls command. The easiest command to start with, is the directory listing command which is used to list the directory contents.

Double-lick to get the command line as shown in the following screenshot. The search result will give the Terminal option. To invoke the command line, go to the search option and enter the command keyword in the search box. In this chapter, we will go through some of the popular command line’s used in Ubuntu.
Ubuntu list directory contents how to#
In conclusion, we have discussed how to set permissions on files & directories using chmod in Ubuntu distribution.Ubuntu is a Linux based operating system and most Linux users are more familiar with the command line interface. Just replace file_name with directory_name. In the same way, we can perform aforementioned operations on directory also. Similarly, for others also – chmod o+rw ABC.txt It is worth mentioning here that, we can use combinations to add permissions to a user and group. Remove permissions for all others – chmod o-r ABC.txt Lastly, for all others – add permissions – chmod o+r ABC.txt Next, to remove permissions for a group – chmod g-r ABC.txt
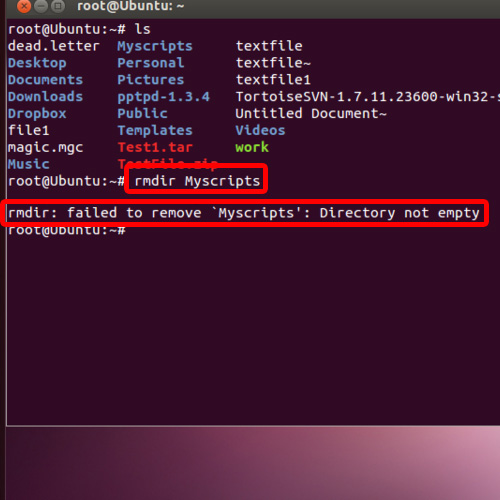
Similarly, to add permission for a group – chmod g+r ABC.txt U-x disallows a user to execute the object U-w is to disallow a user to make modifications to the object U-r is to disallow a user to read the contents of the object To remove permissions for a user, chmod u-r ABC.txt U+w is to allow a user to make modifications to the object U+r is to allow a user to read the contents of the object To add permissions for a user, we can use following combinations – chmod u+r ABC.txt Here, r stands for read, w for write and x for execute Set permissions on files & directories using chmod in Ubuntuįirst, we will discuss user related permissions – this will make modifications to first three characters aforementioned. R- last three characters – only read permissions for others Rw- next three characters – read & write permissions for group Rw- first three characters – read & write permissions for user We define permissions for three set of users namely – user, group and rest others. Now, zeroing down on permission set itself. Output: total 52K drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4.0K Apr 9 08:52 backups drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4.0K cache drwxrwxrwt 2 root. To list file permissions in a folder with human readable file size: ls -lh /var. To list permissions files in a folder including hidden files. rw-rw-r- these are the permissions of the objectġ represent the link count i.e. Output: drwxr-xr-x 15 root root 4096 Apr 23 12:03 /var. With ls -l command, we can view the permissions of an object. It would return us the output – -rw-rw-r- 1 user group 6 Feb 14 00:00 ABC.txt For instance, lets say we have a file ABC.txt then – issue the following in terminal – ls -l ABC.txt We can long list the contents of a file & directory using ls command with -l option. chmod is a command-line utility, which is used to change file mode bits.īut, first we need to discuss a bit about file & directory permissions itself. In this article, we would discuss how to set permissions on files & directories using chmod in Ubuntu distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
